5 Continuous Distributions
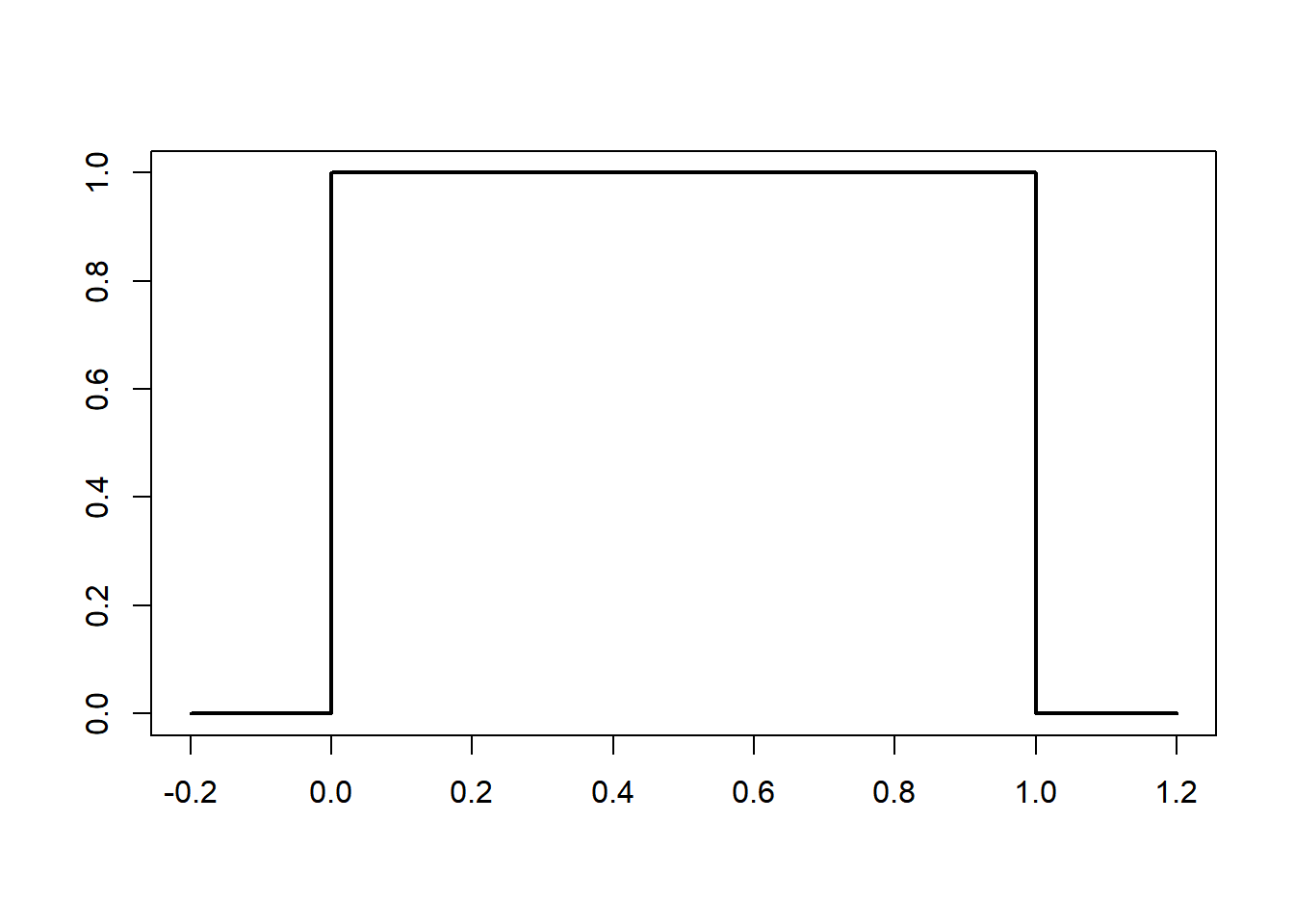
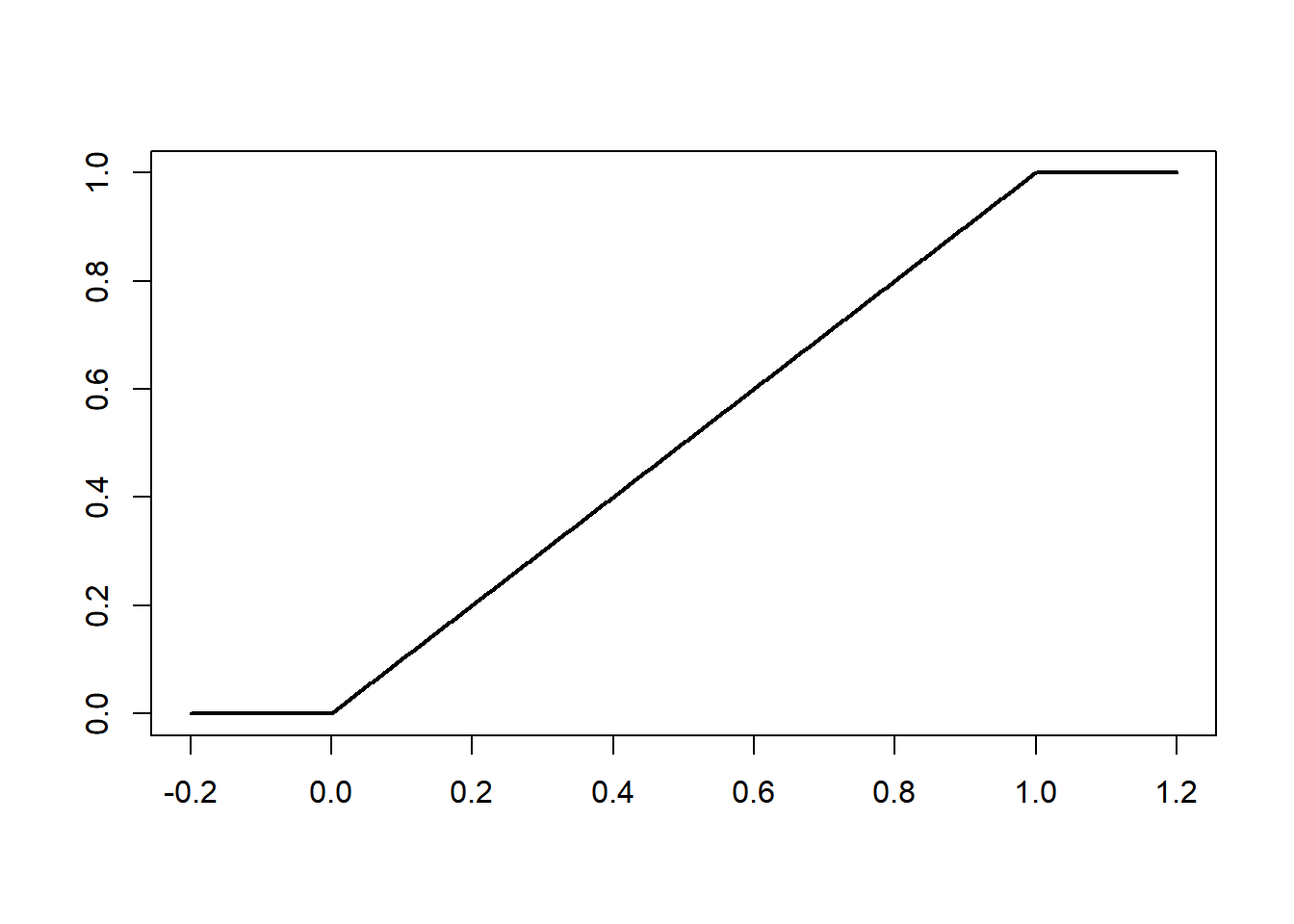
5.1 Uniform distributions
Here is the density and distribution function of the uniform distribution on \([0,1]\).
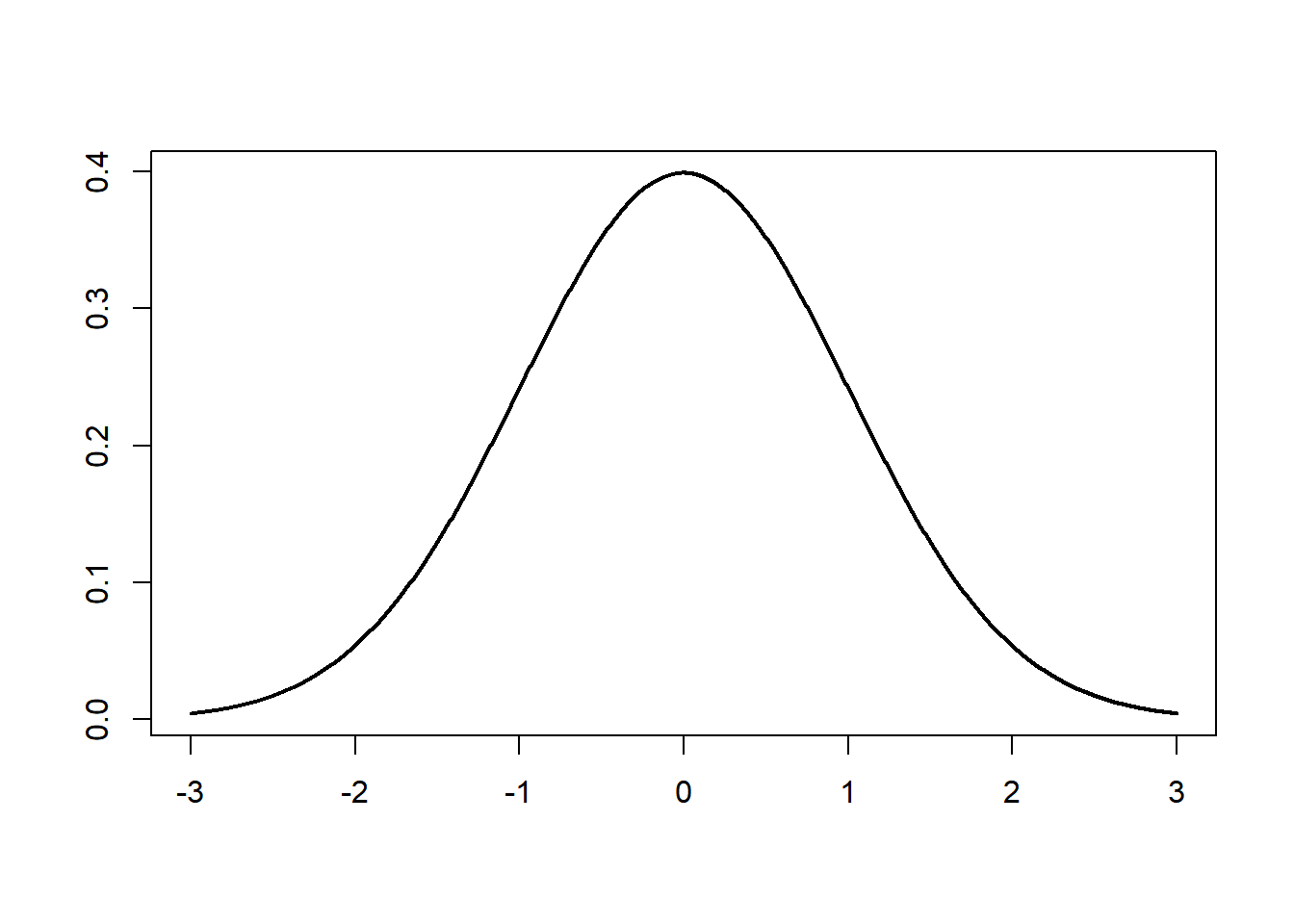
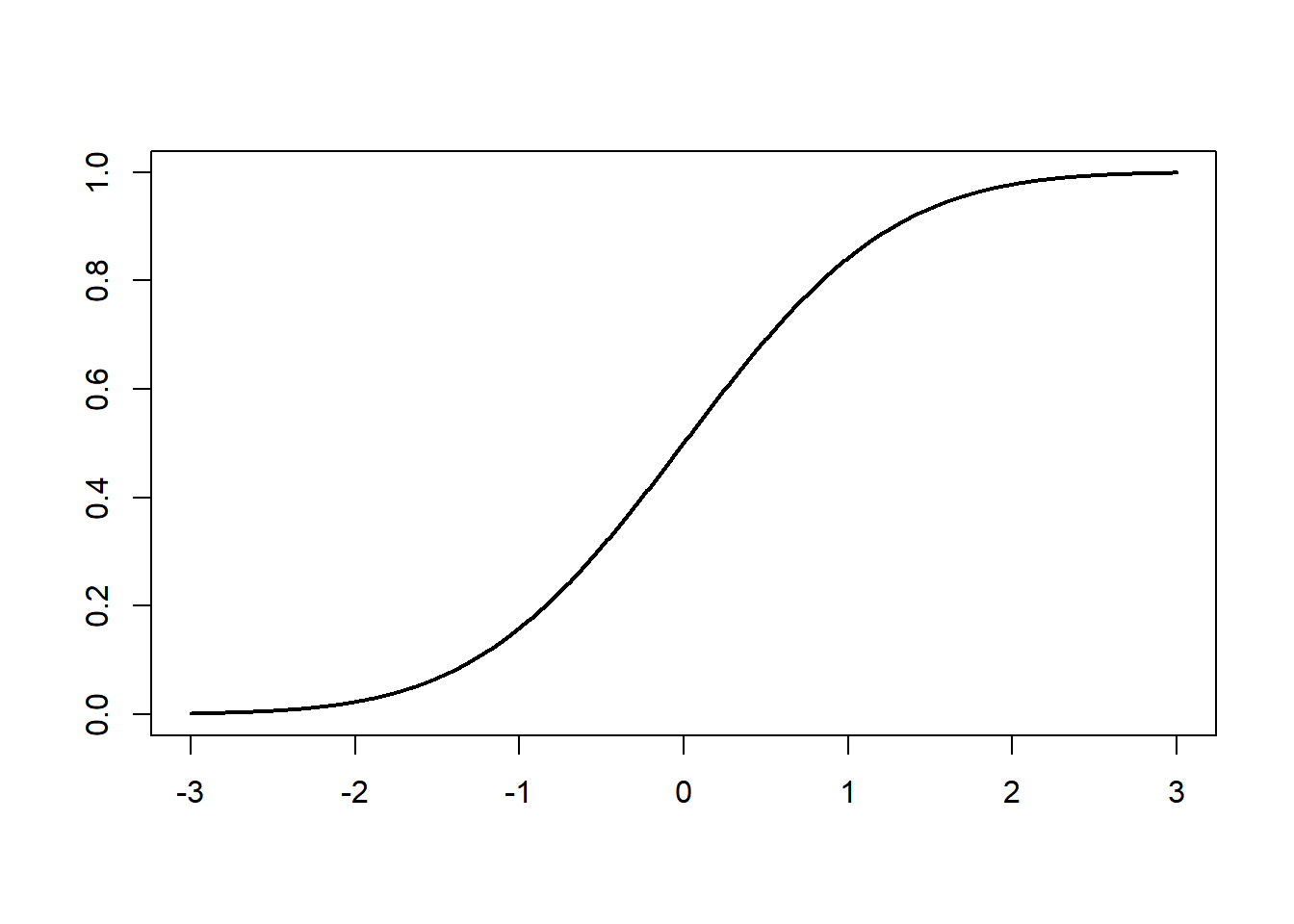
5.2 Normal distributions
Here is the density and distribution function of the normal distribution with mean 0 and variance 1 (i.e., the standard normal distribution).
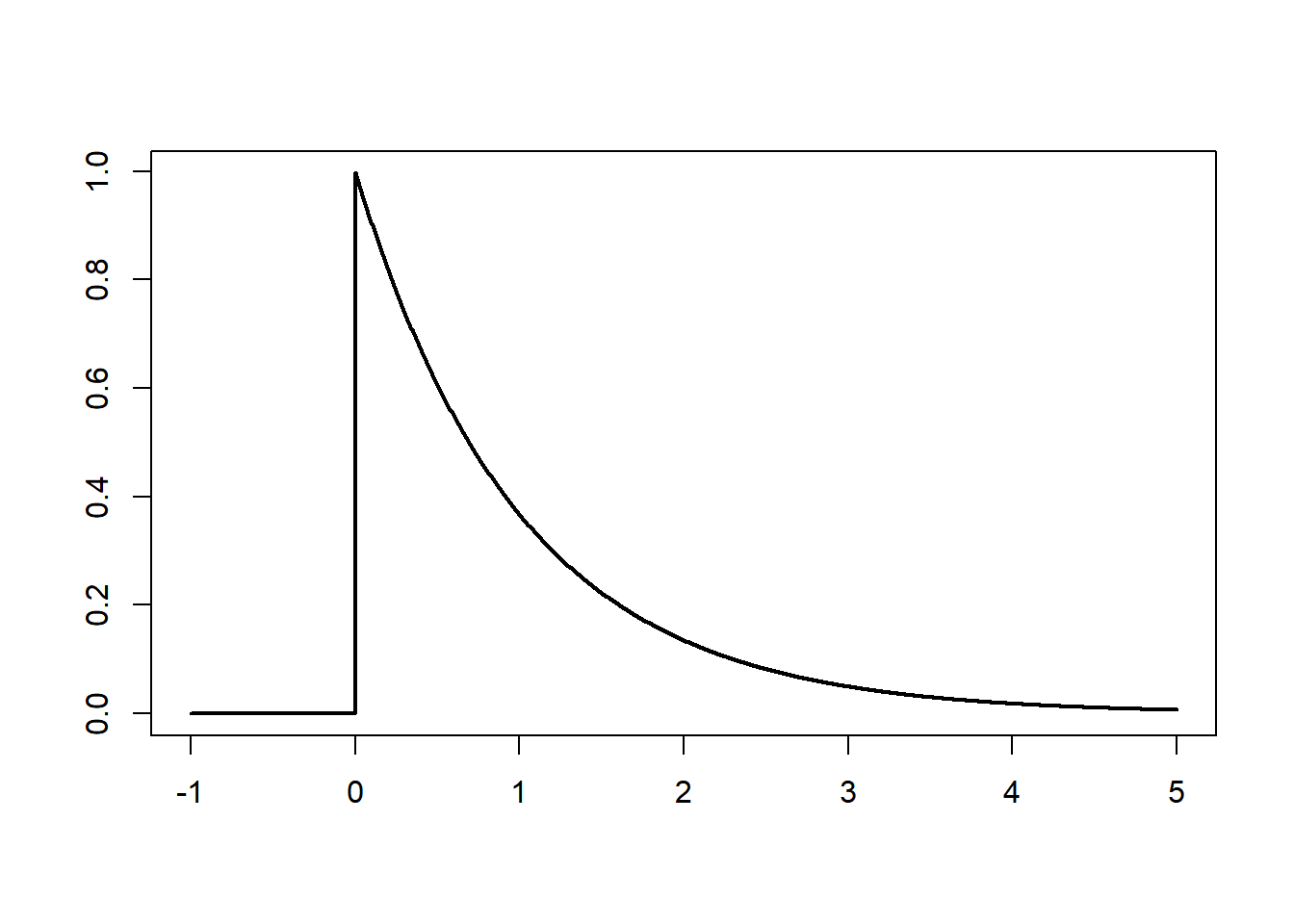
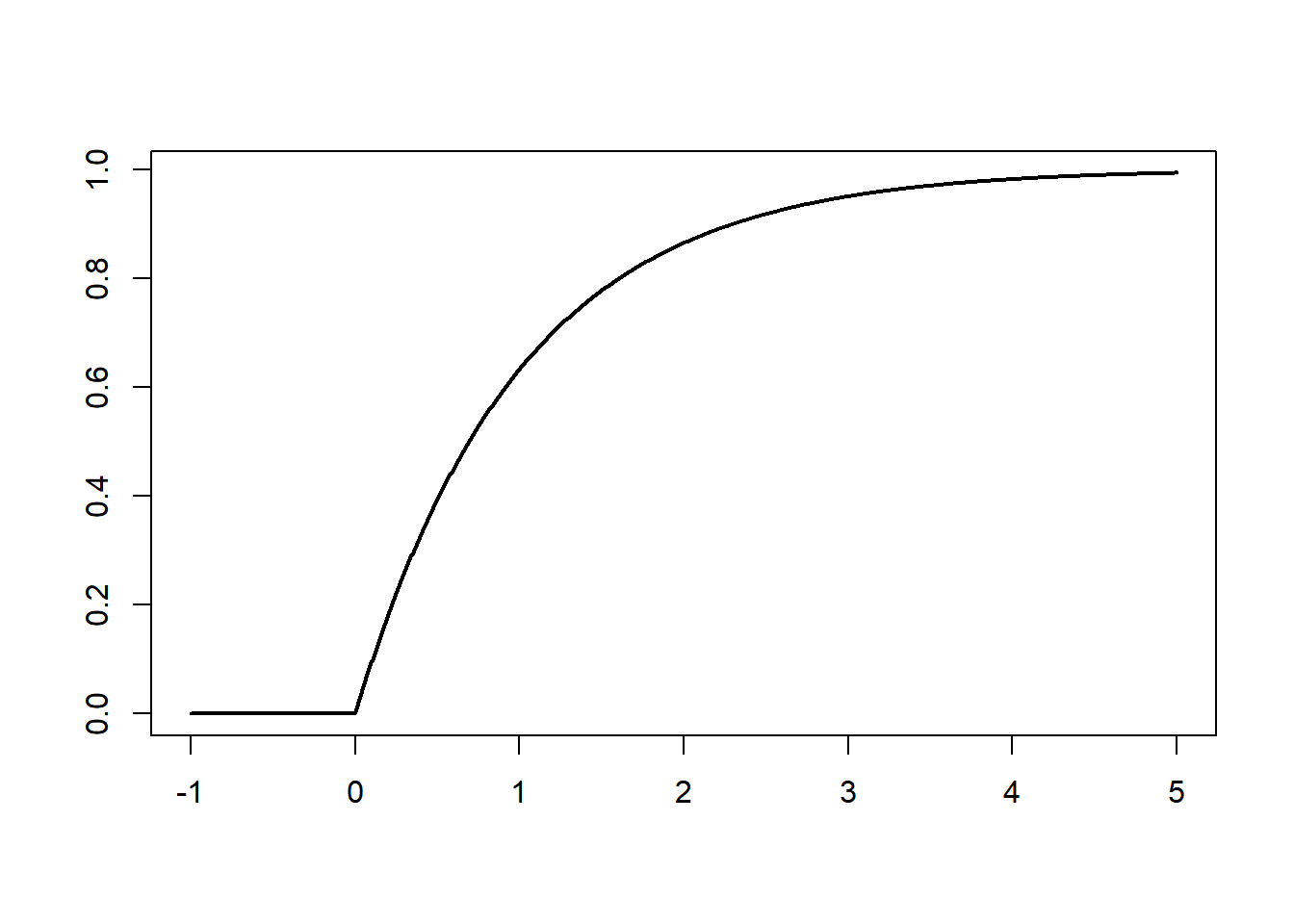
5.3 Exponential distributions
Here is the density and distribution function of the exponential distribution with rate 1.
5.4 Normal approximation to the binomial
The De Moivre - Laplace theorem says that, as n increases while p remains fixed, the binomial distribution with parameters \((n, p)\) is well-approximated with the normal distribution with same mean (\(np\)) and same variance (\(n p (1-p)\)).
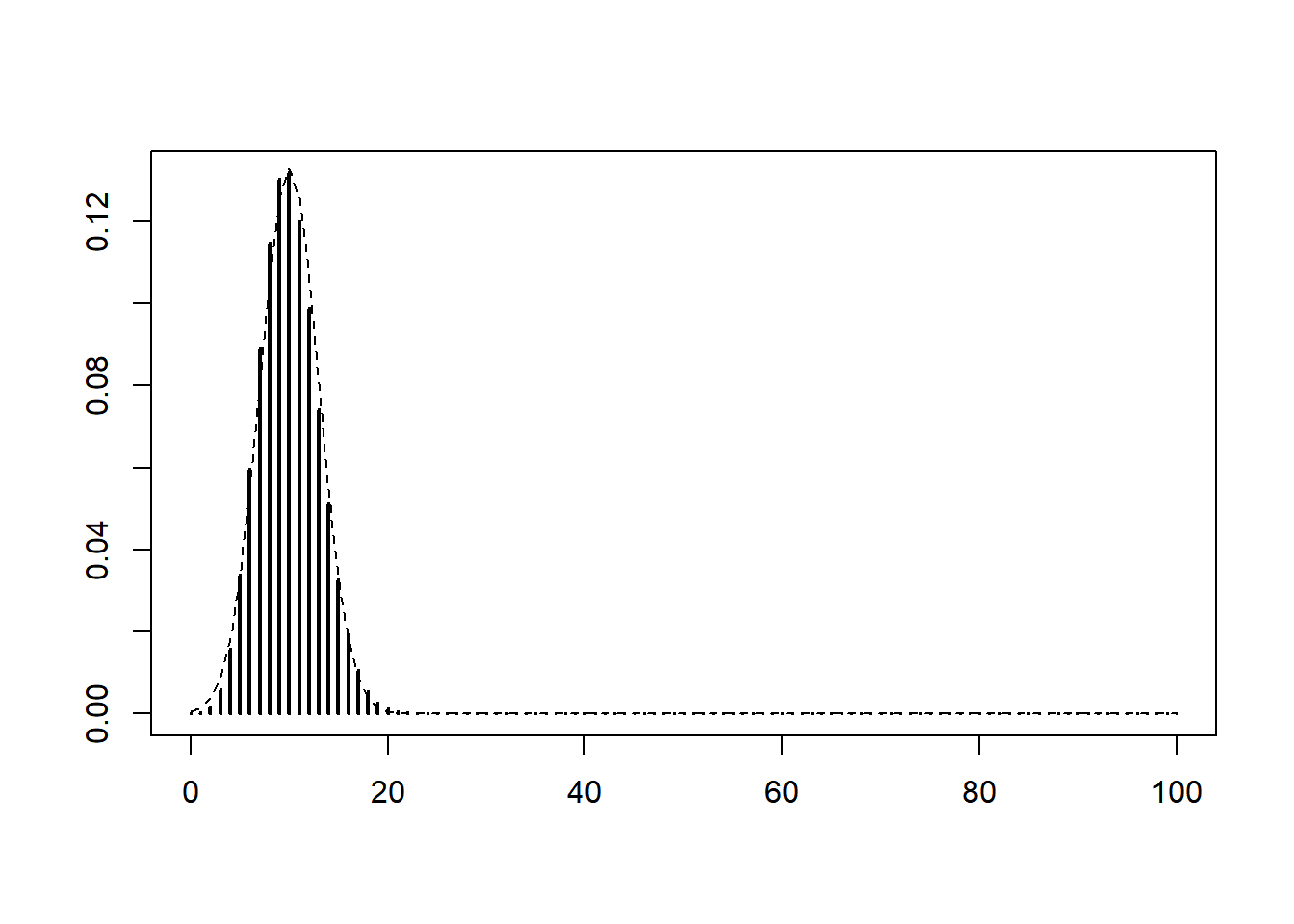
To corroborate this numerically, we fix \(p=0.10\) and vary \(n\) in \(\{10, 30, 100\}\). We can see that the approximation is already very good when \(n=100\).
n = 10
p = 0.1
plot(0:n, dbinom(0:n, n, p), type="h", lwd=2, xlab="", ylab="")
curve(dnorm(x, n*p, sqrt(n*p*(1-p))), add=TRUE, lty=2)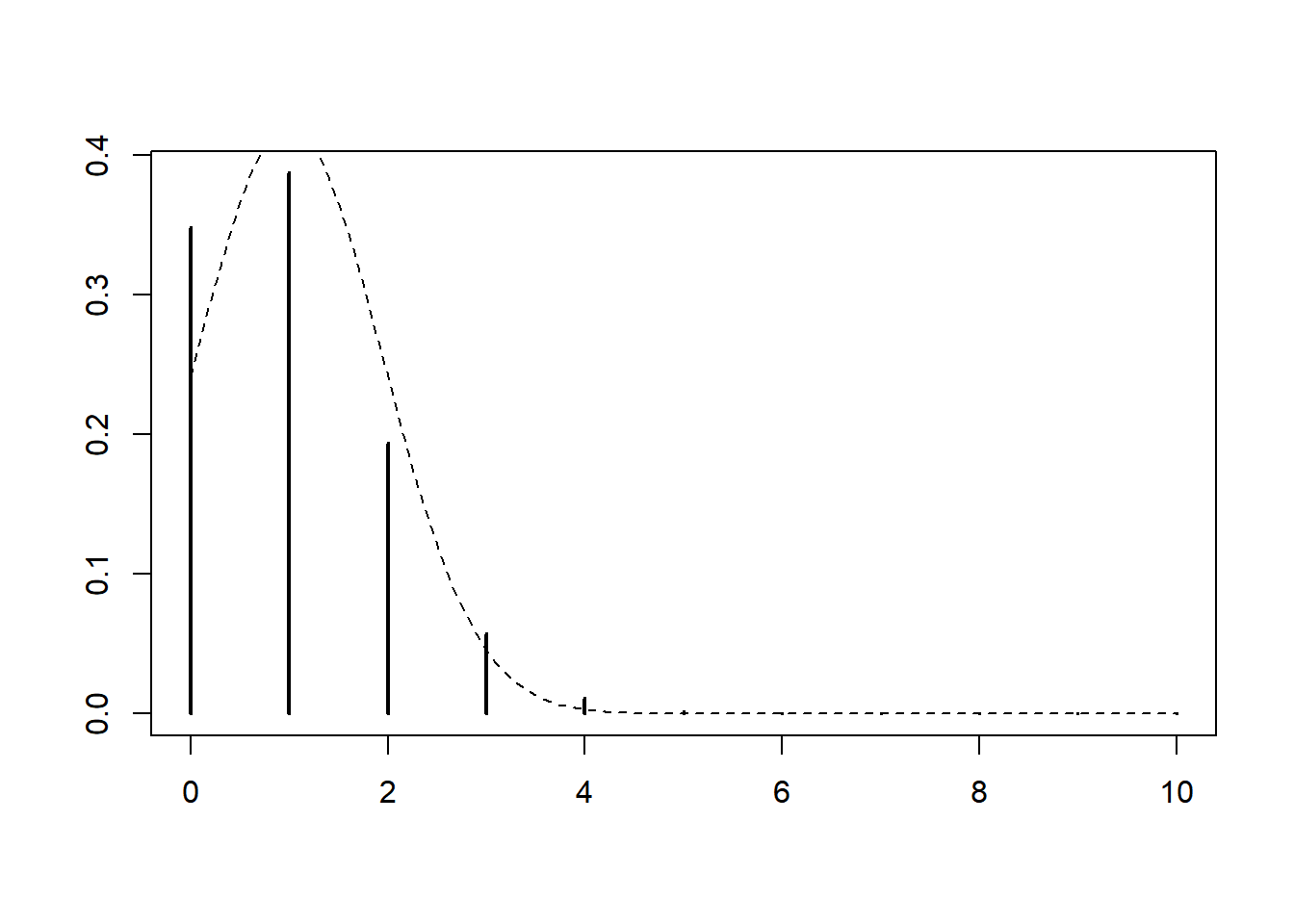
n = 30
p = 0.1
plot(0:n, dbinom(0:n, n, p), type="h", lwd=2, xlab="", ylab="")
curve(dnorm(x, n*p, sqrt(n*p*(1-p))), add=TRUE, lty=2)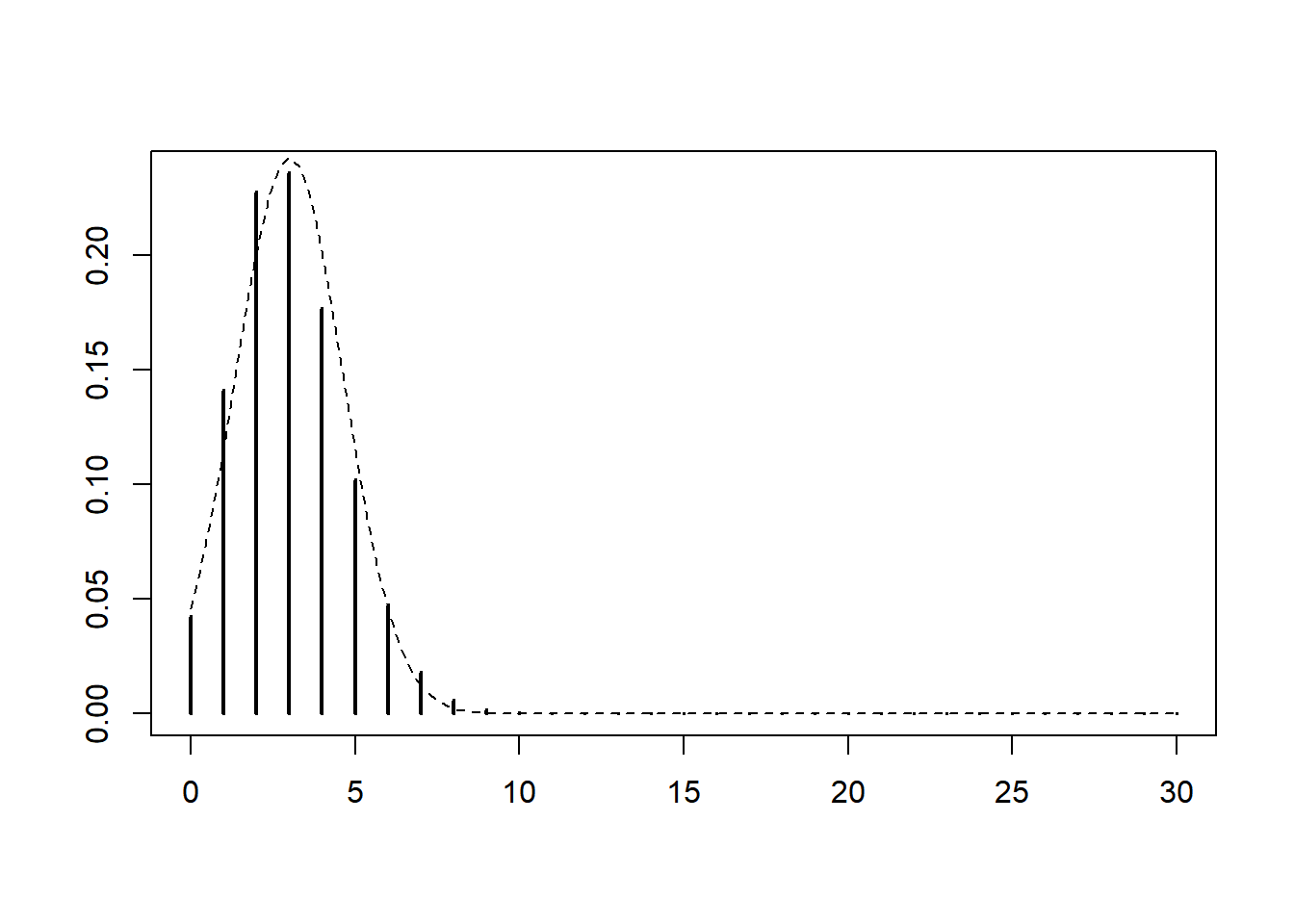
n = 100
p = 0.1
plot(0:n, dbinom(0:n, n, p), type="h", lwd=2, xlab="", ylab="")
curve(dnorm(x, n*p, sqrt(n*p*(1-p))), add=TRUE, lty=2)